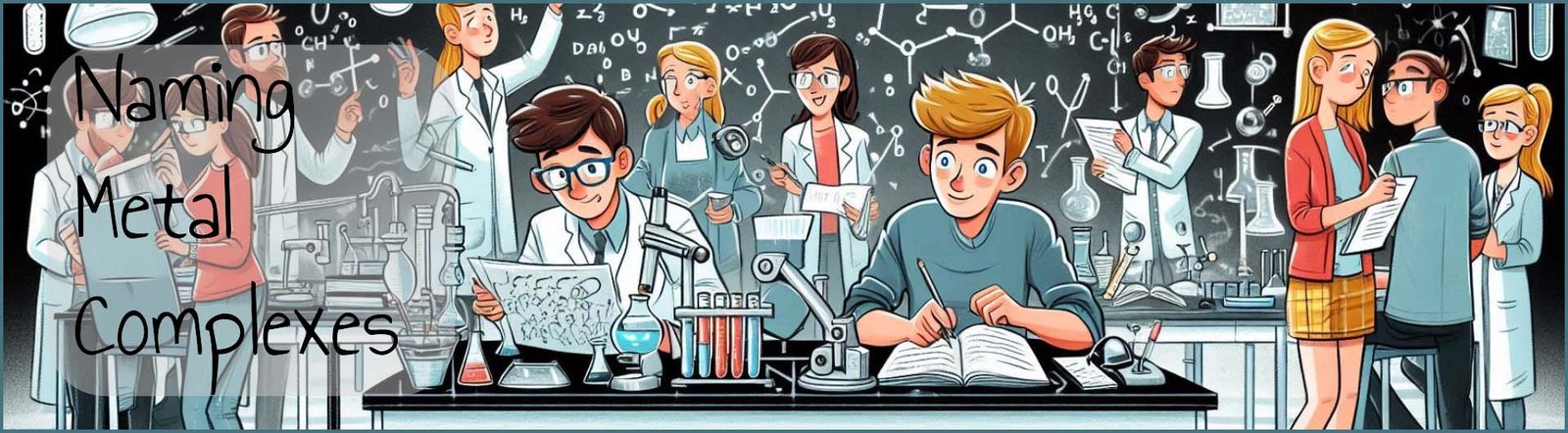

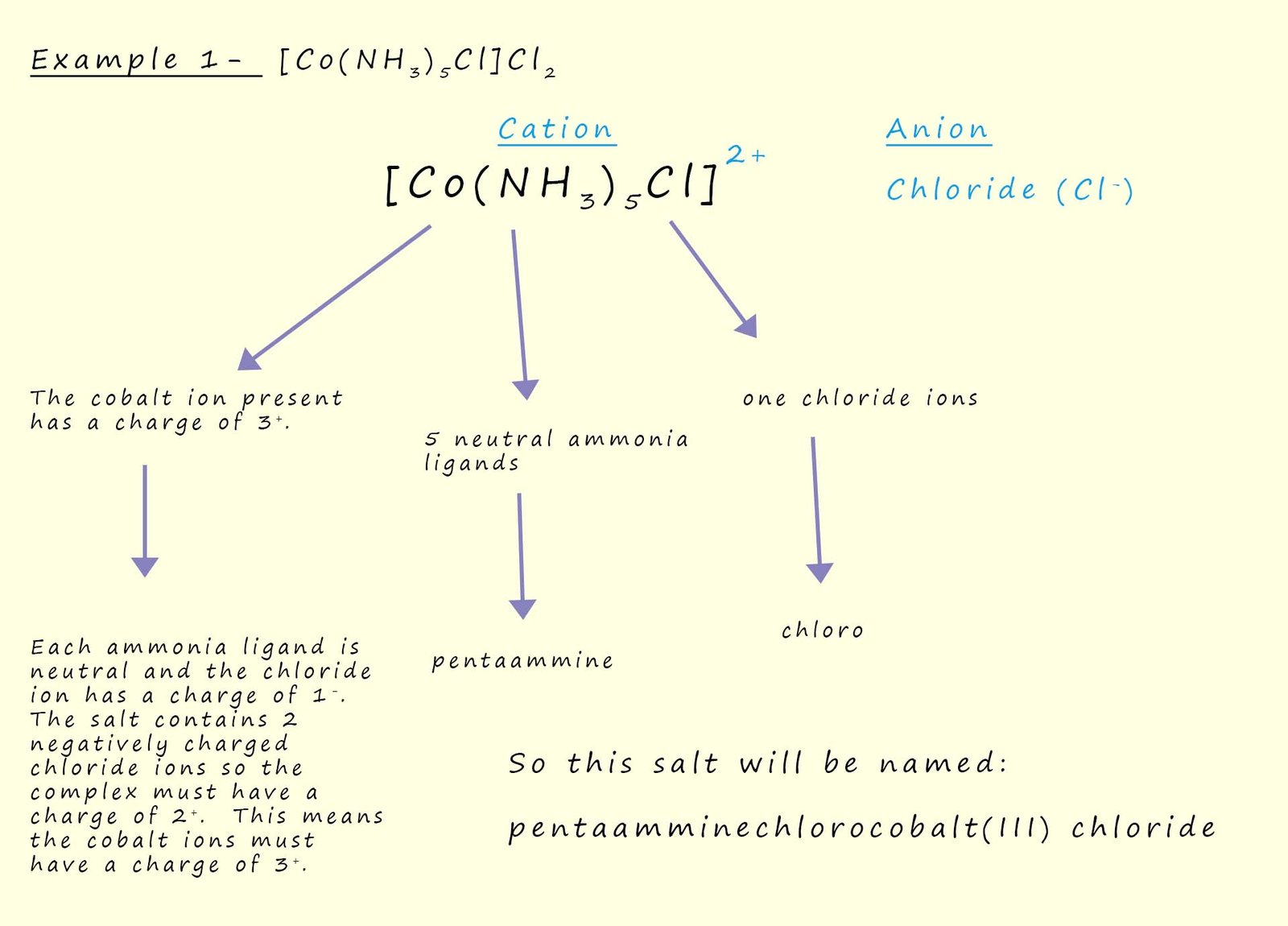
Before we look at the rules and steps involved in naming metal complexes consider the three formulae given below. Each of these examples is an ionic salt or a coordination salt made up of positive and negative ions as you would expect from an ionic compound. The metal complex is shown in square brackets and the other ion/ions present are there to simply balance the charge on the metal complex.

While in the third example the ligand in the metal complex is the bidentate ligand ethylenediamine (NH2CH2CH2NH2) which hopefully you will recall is given the shorthand symbol "en". This salt or coordination compound contains three chloride ions (Cl-), this means that the complex has a charge of 3+ and since the ethylenediamine ligands are neutral ligands the cobalt ion in the complex has a charge of 3+. The complex is therefore cationic.
| Anionic ligand | Ligand name |
|---|---|
| bromide (Br-) | bromo |
| chloride (Cl-) | chloro |
| fluoride (F-) | fluoro |
| hydroxide (OH-) | hydroxo |
| oxide(O2-) | oxo |
| sulfate (SO42-) | sulfato |
| carbonate(CO32-) | carbonato |
| cyanide(CN-) | cyano |
| oxalate(C2O42-) | oxalato |
* Note- The oxalate ion (C2O42-) is also known as ethanodioate. You will need to consider this when you come to name complexes containing this bidentate ligand, you will need to use the prefixes bis, tris if more than one oxalate ion is present.
| Ligand | Ligand name |
|---|---|
| ammonia (NH3) | ammine |
| water (H2O) | aqua |
| carbon monoxide(CO) | carbonyl |
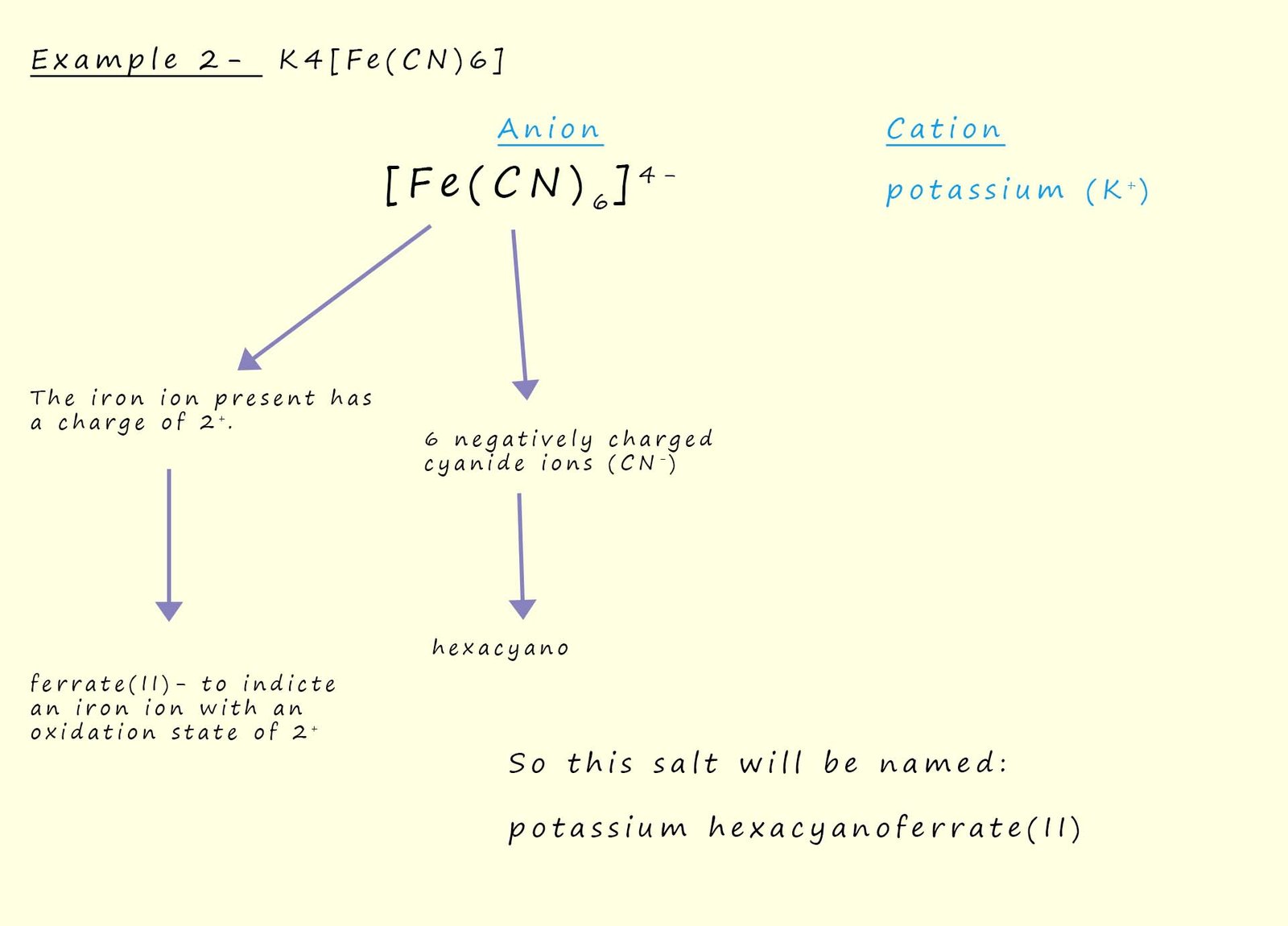
The second salt we had to name from the examples above has the formula K4[Fe(CN)6],
this time the complex [Fe(CN)6]4- will have an overall charge of 4-, we know this because there are four potassium ions (K+) in the formula for the salt and each of these ions has a +1 charge. Now the complex also contains six cyanide ions (CN-) each of which has a 1- charge, this obviously means that the six cyanide ions will contribute an overall charge of -6, so in order for the complex to have an overall charge of 4- the iron ion present must have a charge of 2+ (Fe2+).
| Metal name | Latin name | Metal name in anionic complex |
|---|---|---|
| iron | ferrum | ferrate |
| copper | cuprum | cuprate |
| gold | aurum | aurate |
| tin | stannum | stannate |
| silver | argentum | argentate |
| manganese | manganese | manganate |
| vanadium | vanadium | vanadate |
So to name the salt K4[Fe(CN)6] simply follow the rules outlined above, taking into account that the complex in this example is anionic, the method used is outlined below:
To name the final complex [Co(en)3]Cl3 requires one more rule, now we stated in rule 3 that the Greek prefixes di, tri, tetra, penta and hexa were used to indicate the number of ligands attached to the central metal ion in a complex, however if the name of the attached ligand already uses one of these Greek prefixes; as is the case with ethylenediamine then an alternative system is used to indicate the number of attached ligands, here the number of attached ligands is indicated using the prefixes bis (2), tris (3), tetrakis (4), pentakis (5) and hexakis (6). So the salt [Co(en)3]Cl3 will be named: tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) chloride.